API Plan 72
Externally supplied buffer gas maintained at a pressure less than the seal chamber pressure.
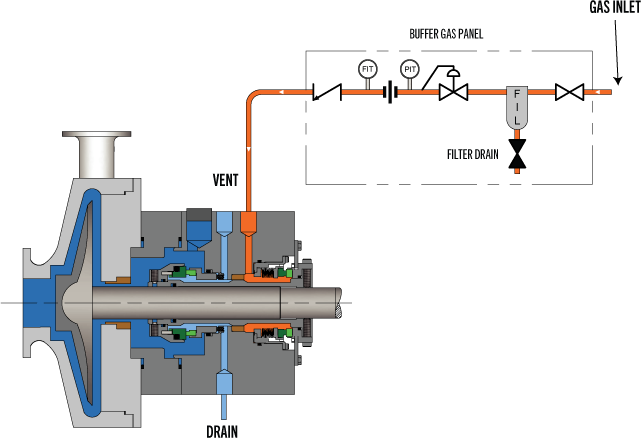
Description
This plan uses an externally supplied, low-pressure buffer gas (usually nitrogen) that is injected into the outer seal cavity. The injection process is regulated by a control panel for optimal results.
Application Notes
- Used in Arrangement 2 dual unpressurized seals, where the buffer medium is a gas. In normal operation, the buffer gas pressure should not exceed 10 psi [0.7 bar].
- Plan 72 may be used alone or partnered with a Plan 75 (for condensing leakage) or Plan 76 (for non-condensing leakage).
- Forward pressure regulator should be set to at least 5 psi [0.4 bar] above the normal flare pressure.
- Most common buffer gas is nitrogen. Ensure a reliable supply and avoid the use of bottles if possible.
- Buffer gas can be used to sweep inner seal leakage away from outer seal into a collection system and/or dilute the leakage so the emissions from the containment seal are reduced.
- Ensure vent port is oriented to the 12 o’clock position and the drain is oriented to the 6 o’clock position.
- Buffer gas can act to prevent icing in cryogenic applications.
Pros:
- Reduction in fugitive emissions due to the buffer effect of nitrogen
- Prevention of icing in cryogenic applications
- This plan provides some cooling at the outboard seal
Cons:
- Loss of buffer gas will cause a rise in emissions
